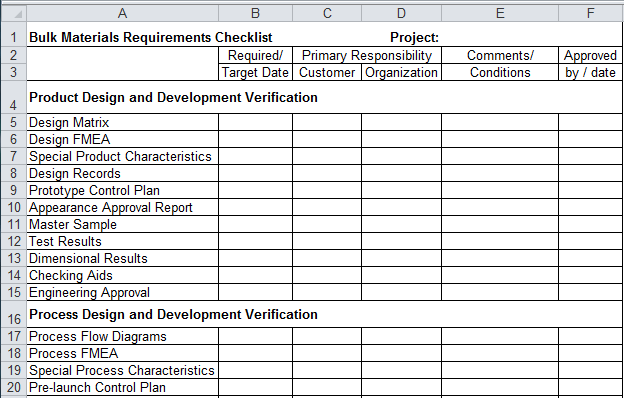
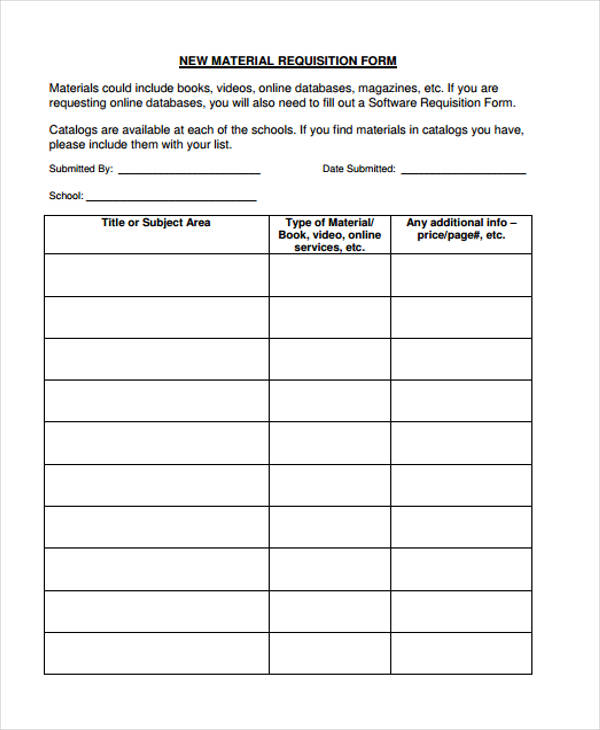
What is material requirements planning? How much is required at a time? This is a form used to request items from a company or organization’s inventory so that those items can be used for a project or for providing service to a customer or client. You can modify these formats as your requirement.
Material requirement planning (MRP) is a key element in managing resources in a manufacturing environment. It will help the companies manage dependent demand inventory and schedule replenishment. MRP is concerned with both production scheduling and inventory control. It is a material control system that attempts to keep adequate inventory levels to assure that required materials are available when needed.
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a computer-based production planning and inventory control system. MRP is a simple system of calculating arithmetically the requirements of the input materials at different points of time based on the actual production plan. MRP can also be defined as a planning and scheduling system to meet time-phased materials requirements for production operations.
MRP converts the master schedule of production into a detailed schedule, so that you can purchase raw materials and components. Used mostly in the manufacturing and fabrication industries, this system is a push type of inventory control, meaning that organizations use forecasting to determine the customer demand for products. The manufacturing or fabrication company will forecast the amount and type of products they will purchase, along with the quantity of materials to produce them. They then push the products to the consumers.
This contrasts with a pull system, where the customer first places an order. The main disadvantage of a push system is its vulnerability when sales vary. In this scenario, the forecasts become inaccurate, which for manufacturing, cause either a shortage of inventory or an excess of inventory that requires storage. See full list on smartsheet.
In determining how much material your product needs, MRP differs from consumption-based planning (CBP). MRP logic uses information received either directly from customers or from the sales forecast, calculating the material required based on the dependencies of other materials. CBP calculates material requirements only via historical consumption data.
CBP does not consider the dependencies between different materials, as it presumes that future consumption will follow the same pattern that the historical data did. For all companies, MRP has a few goals in common. There are some terms that will come up in MRP repeatedly. Some are terms related to MRP as a concept, and some are specific to MRP software.
You may use MRP concepts in a variety of different production environments. You may also use them for service providers, such as job shops. Examples of production environments include instances in which products are complex, products are only assembled to order, or demand items are discrete and dependent.
This more accurate scheduling improves your companys productivity by decreasing the necessary lead time, giving your customers a higher quality of production and service. Overall, your company is more competitive in the marketplace. However, with these advantages come a few drawbacks.
Foremost, MRP is only successful if the accounting is accurate. You must keep records of inventory and BOM changes up to date. Inaccurate input causes inaccurate output.
Another potential downside to MRP is that it can be costly. If you dont keep the input in a timely fashion, it can be difficult and expensive when switching over to a new system. An MRP system can completely transform a companys operational procedures.
The MRP technique can be vague at times because we call it a calculation process without necessarily indicating how to compute the data outputs. MRP is about putting mathematical controls into place using formulas that yield optimal. MRP is an optimal control problem that calculates the initial conditions, the dynamics, the constraints, and the objective.
The variables are the local inventory, the order size, the local deman the fixed order costs, the variable order costs, and the local inventory holding costs. MRP comprises many methods and calculations. To find the order quantities, you can use any number of methods.
Although using an MRP system is vastly superior to cobbling together a system of spreadsheets and hand calculations, problems do arise. The biggest issue is data integrity. Data that is either not up to date or has errors gives output that is inaccurate and can end up costing your business serious money.
You should carefully screen inventory and BOM data. Errors often occur during cycle-count adjustments, input and shipping, and reporting of scrap, damage, waste, and production. Barcode scanning and pull systems can minimize these types of errors. Moreover, MRP systems can be rife with error when companies with facilities in different countries do not set up by individual location.
For example, the MRP system could indicate that there is plenty of raw material available for production when, in fact, that raw material is on the other side of the world. Staffpower is also not always accounted for in MRP. In addition, lead times can throw off MRP. In these cases, the MRP creates a capacity issue.
The required lead time can change based on the product. MRP assumes that the lead time is always the same for each product, regardless of changes in supply, required quantities, or the possible simultaneous production of other products. Solving your data-integrity issues may take some concentrated effort.
During the early part of the 20th Century, material and planning control systems started using mathematics to calculate manufacturing lot sizes. Harris introduced the economic order quantity (EOQ) model, and it is still studied today for inventory management. Orlicky was on a mission to educate senior executive customers to use computer technology to manage their inventory and control processes.
Long considered a bible of production and inventory control practices, the books influence was almost immediate. The three professionals, Orlicky, Wight, and Plossl began the movement that saw nearly 7companies adopt MRP by the time Dr. The next generation of MRP was considered closed-loop MRP, because it added a feedback feature that enabled the synchronization and adjustment of the master production schedule, effectively closing the loop. Helmed by the three professionals, APICS, formerly the American Production and Inventory Control Society, undertook a huge campaign called the MRP Crusade to tout the benefits of the MRP system and make it the standard for manufacturing planning in America. Still going strong, APICS now serves as a professional association for supply-chain operations, logistics, and management research and publications.
Considered a significant innovation, MRP II includes additional data, such as employee and finance information. This edition introduced demand-driven MRP (DDMRP), with five components, including strategic inventory positioning, buffer profiles, level, dynamic adjustments, demand-driven planning, and highly visible and collaborative execution. Specific to the manufacturing industry is manufacturing resource planning (MRP II). MRP was so successful that organizations using it wanted more improvements and more automation.
MRP II takes the principles of MRP and adds some additional areas, such as rough-cut capacity planning and capacity requirement planning (CRP), to give companies a comprehensive manufacturing plan. MRP II also relies on the quality and timeliness of the inputted data. CRP takes data from MRP.
These plans can lead to execution failure and even reimplementation. MRP is a planning and control system for the resources in a company and was essentially the harbinger of ERP systems to come. ERP is a solution for the enterprise as a whole, with more functionality built in, extending the concepts of MRP and MRP II. All the functions in an enterprise are tightly integrate including internal and external information.
For example, an ERP system would possess advanced functionality in the areas of financial , customer relationship, and sales order management. DRP takes MRP one step further and calculates how to move the materials out of the facility. The product delivery is more efficient because DRP calculates the quantity of each type of goods that requires delivery, as well as where to meet the demand. DRP is a time-based approach to guarantee that inventory thats likely to be low has a replenishment plan. DRP is similar to MRP but can work by either a push or pull system.
Now, DRP can still be a stand-alone system or act as a module within an ERP system. Using an ERP system gives your company some strategic opportunities. Companies report that the biggest benefits of their ERP system are increased efficiency, integrated information, more customized reports, higher-quality customer service, and more secure data.
A well-used ERP system can enable your teams to be forward-looking and support your strategic vision for growth. A good ERP strategy improves your key business processes. I was involved in implementing ERP systems for various manufacturers. MRP was an essential part for production planning and scheduling and was an integral part for ensuring the materials were ordered on time to meet customer demand. It is essential to have all the parameters set up correctly, such as manufacturing lead times and safety stock, to make sure that the resulting MRP recommendations are accurate.
For example, if product includes wrong manufacturing or purchasing lead times, MRP will recommend starting production on a wrong date, and that can result in product being produced later than the customer demands it. This can result in loss of customers and decrease in revenue. Although MRP is often an integrate automated system, it can also be handwritten or consist of different applications or modules in disparate software systems. MRP software focuses on the period during which you create a product, identify and purchase raw materials , determine resources, and plan the steps for production. This subset of modern ERP systems is usually available as a module and looks for efficiencies in each step.
The cost of MRP software is a big concern for small businesses, but its clear that the investment is a huge money saver in the long run. Furthermore, your business may fiscally require a software system due to the risk of human error, slowed production times, and excessive manual labor costs. Still, companies need to consider what type of software is most appropriate for them category-wise, size-wise, and expectations-wise.
For a small business, purchasing a comprehensive ERP suite may not only be wasteful, but also time-inefficient, defeating the systems purpose. Contact our team to learn how Smartsheet can help manufacturing organizations amplify their efforts, or simply check out our Smartsheet for Manufacturing solution page. Most MRP systems are software-base but it is possible to conduct MRP by hand as well. A material advisor can be an individual, trust, estate, partnership, or corporation.
Header section: Date of requisition. An MRP integrates data from production schedules with that from inventory and the bill of materials ( BOM ) to calculate purchasing and shipping schedules for the parts or components required to build a product. In order to cover these requirements , MRP does net requirement calculation and plans procurement quantities and dates on which the material needs to be procured or produced.
Check Required Email:. So just like that, we have implemented a Reactive Angular Form with Angular Material and Bootstrap and we have also declared our own validator function. The first paragraph states the purpose of the letter while the second lists relevant information and suggestions about the use stated.
End the letter courteously.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.